Updated Medical Opinion Signs and Symptoms of Depression: What You Need to Know
Depression is a common mental health disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It goes beyond feeling sad or having a bad day; depression is a persistent condition that can interfere with your daily life and overall well-being. Understanding the signs and symptoms of depression is crucial for early detection and effective treatment. In this article, we’ll explore the key indicators of depression, helping you recognize them in yourself or others. Specialist have come back to the subject and combined multiple research and new analysis which we have summarize in this article.
What Is Depression?
Depression is a mood disorder characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a lack of interest or pleasure in activities that were once enjoyable. It affects how you feel, think, and behave, leading to various emotional and physical problems. Depression can vary in severity, from mild to severe, and can impact anyone, regardless of age, gender, or background.

Common Signs and Symptoms of Depression
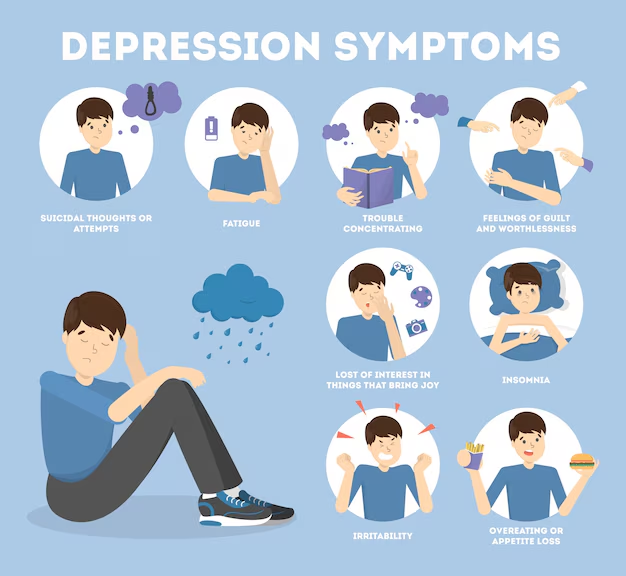
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of depression is the first step in seeking help. While symptoms can vary from person to person, some common indicators include:
- Persistent Sadness: Feeling sad, empty, or hopeless for most of the day, nearly every day.
- Loss of Interest: A marked decrease in interest or pleasure in activities you once enjoyed, including hobbies, social activities, and sex.
- Fatigue and Low Energy: Feeling constantly tired or lacking energy, even after adequate rest.
- Sleep Disturbances: Experiencing insomnia, waking up too early, or oversleeping.
- Changes in Appetite or Weight: Significant weight loss or gain due to changes in appetite.
- Difficulty Concentrating: Trouble focusing, making decisions, or remembering details.
- Feelings of Guilt or Worthlessness: Excessive guilt, self-blame, or feelings of worthlessness.
- Irritability or Restlessness: Becoming easily agitated or feeling restless and unable to sit still.
- Physical Aches and Pains: Unexplained physical symptoms, such as headaches, digestive issues, or chronic pain.
- Thoughts of Death or Suicide: Recurrent thoughts of death, suicidal ideation, or attempts.
Understanding the Severity of Symptoms
Depression can manifest in various ways, from mild episodes that temporarily disrupt your life to severe cases that make it difficult to function. It’s essential to pay attention to how these symptoms impact your daily life and relationships. If you notice that these signs persist for more than two weeks, it may be time to seek professional help. In this new generation, depression can come from many twisted angles and some times you might not even notice.
Risk Factors for Depression
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing depression, including:
- Genetics: A family history of depression or other mental health disorders.
- Biological Factors: Imbalances in brain chemicals, such as serotonin and dopamine.
- Trauma or Stress: Experiencing traumatic events, prolonged stress, or significant life changes.
- Chronic Illness: Managing long-term health conditions or chronic pain.
- Substance Abuse: Alcohol or drug abuse can exacerbate symptoms of depression.
- Personality Traits: Low self-esteem, pessimism, or being overly self-critical.

When to Seek Help
If you or someone you know is experiencing signs of depression, it’s crucial to seek help as soon as possible. Depression is a treatable condition, and early intervention can lead to better outcomes. Here are some steps to take:
- Talk to a Healthcare Provider: Discuss your symptoms with a doctor, therapist, or psychiatrist.
- Reach Out to Support Networks: Connect with friends, family, or support groups who can offer understanding and encouragement.
- Consider Therapy: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), interpersonal therapy (IPT), and other forms of counseling can be effective in treating depression.
- Medication: Antidepressants may be prescribed to help balance brain chemicals and alleviate symptoms.
Conclusion
Depression is a serious condition that requires attention and care. By recognizing the signs and symptoms early, you can take the necessary steps to manage and treat depression effectively. Remember, you don’t have to go through this alone. Help is available, and recovery is possible with the right support and treatment. If you or someone you know is struggling with depression, reach out to a healthcare professional today.
Comments
Post a Comment